General information
Content Type
If not otherwise stated, OctoPrint’s API expects request bodies and issues response bodies as Content-Type: application/json.
Encoding
OctoPrint uses UTF-8 as charset.
That also includes headers in multipart/form-data requests, in order to allow the full UTF-8 range of characters
for uploaded filenames. If a multipart/form-data sub header cannot be decoded as UTF-8, OctoPrint will also attempt
to decode it as ISO-8859-1.
Additionally, OctoPrint supports replacing the filename field in the Content-Disposition header of a
multipart field with a filename* field following RFC 5987, Section 3.2,
which allows defining the charset used for encoding the filename. If both filename and filename* fields are
present, following the recommendation of the RFC filename* will be used.
For an example on how to send a request utilizing RFC 5987 for the filename* attribute, see the second example
in Upload file.
Cross-origin requests
To make use of the OctoPrint API from websites other than the OctoPrint web interface, cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) must be enabled. This is the case even when the website in question is served from a different port on the same machine and on localhost.
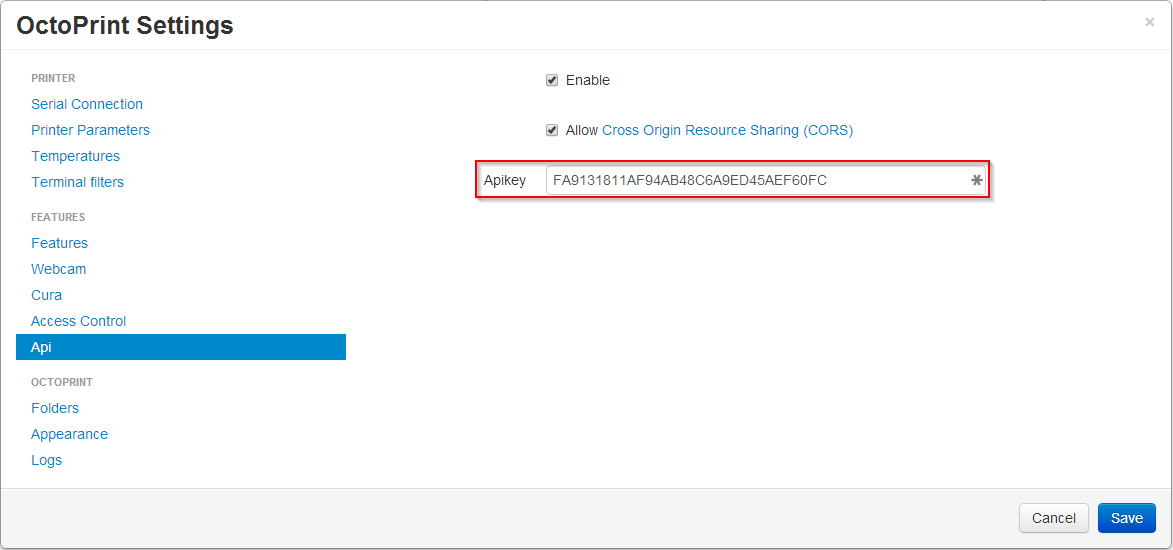
To enable this feature, set the allowCrossOrigin key of the api section in config.yml to true or
check the corresponding checkbox in the API settings dialog.
api:
enabled: true
key: ...
allowCrossOrigin: true
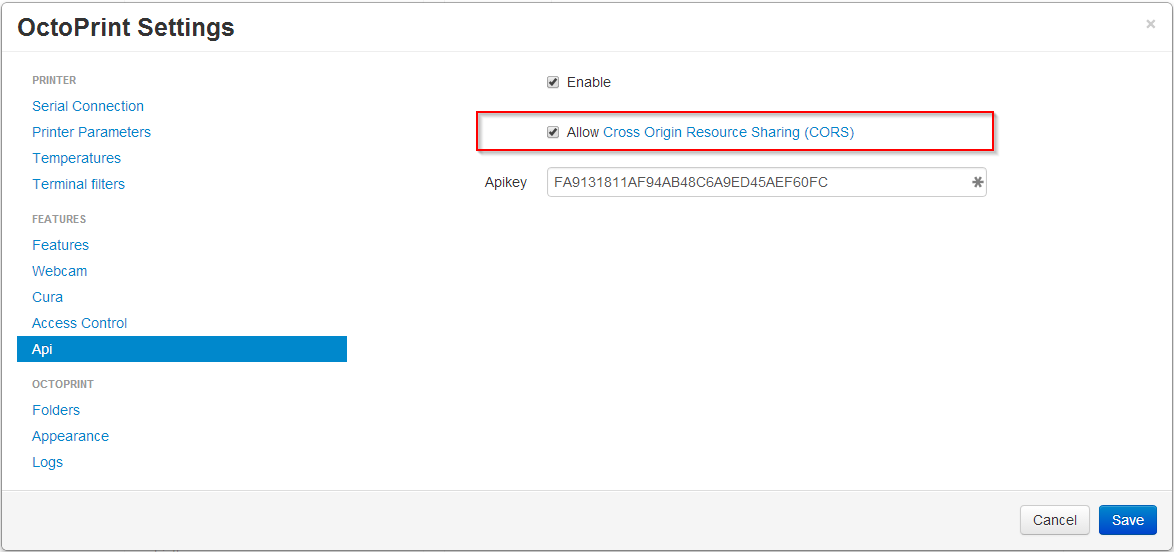
Fig. 25 Support for CORS can be enabled in the “API” settings
Warning
This means any browser page can send requests to the OctoPrint API. Authorization via an API-Key is still required however.
If CORS is not enabled you will get errors like the following:
XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://localhost:8081/api/files. No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin'
header is present on the requested resource.
Note
For security reasons, OctoPrint will not set the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials
header, even if CORS support is enabled. That means that cookies will not be sent by
the browser to OctoPrint, effectively making it impossible to authenticate through
the login mechanism (or reusing an existing login session). When accessing OctoPrint
via CORS, you’ll therefore always need to use an API key.
CSRF Protection
Added in version 1.8.3.
To protect OctoPrint against CSRF attacks against the non CORS affected upload endpoints, in case of browser session based authorization the API
is protected using the Double Submit Cookie mitigation strategy.
On first page load of the UI, the login page or the recovery page, a csrf_token_P<port> or csrf_token_P<port>_R<root> cookie is set
that can be read via client-side JavaScript. All requests towards the API that are not GET, HEAD or OPTIONS
and rely on cookie based authorization (so not on an API key but rather an active login session) are required
to send both the csrf_token cookie as well as an X-CSRF-Token header containing its value.
Note
If you use the JS Client library, this will take care of doing the needful for you. Any code in the Core UI calling
API functions through $.ajax or $.get or $.post will also take care of this for you. If you use another library for
accessing OctoPrint’s API in a browser context, you’ll need to make sure to send the X-CSRF-Token header yourself. Examples for
several JS frameworks can be found in the OWASP cheatsheet on CSRF attacks.
Take a look at the implementations of OctoPrintClient.getCookie and OctoPrintClient.getHeaders in src/octoprint/static/js/client/base.js
for details on how to retrieve the cookie value and how to construct the header.
Login
- POST /api/login
Creates a login session or retrieves information about the currently existing session (“passive login”).
Can be used in one of two ways: to login a user via username and password and create a persistent session (usually from a UI in the browser), or to retrieve information about the active user (from an existing session or an API key) via the
passiveflag.Will return a 200 OK with a login response on successful login, whether active or passive. The active (username/password) login may also return a 403 Forbidden in case of a username/password mismatch, unknown user or a deactivated account.
Warning
Previous versions of this API endpoint did return a 401 Unauthorized in case of a username/password mismatch or an unknown user. That was incompatible with basic authentication since it was a wrong use of the 401 Unauthorized code and got therefore changed as part of a bug fix.
Note
You cannot use this endpoint to login from a third party page via CORS, see above. You can however use it to retrieve user information via passive login with an API key (e.g. if you need the
sessionto authenticate on the web socket.- JSON Parameters:
passive – If present, performs a passive login only, returning information about the current user that’s active either through an existing session or the used API key
user – (active login only) Username
pass – (active login only) Password
remember – (active login only) Whether to set a “remember me” cookie on the session
- Status Codes:
200 OK – Successful login
403 Forbidden – Username/password mismatch, unknown user or deactivated account
Logout
- POST /api/logout
Ends the current login session of the current user.
Only makes sense in the context of browser based workflows.
Will return a 204 No Content.
- Status Codes:
204 No Content – No error
Current User
- GET /api/currentuser
Retrieves information about the current user.
Will return a 200 OK with a current user object as body.
- Status Codes:
200 OK – No error
Data model
Login response
The Login response is a user record extended by the following fields:
Name |
Multiplicity |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
string |
The session key, can be used to authenticate with the |
|
1 |
boolean |
Whether the client that made the request got detected as external from the local network or not. |
Current user
Name |
Multiplicity |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
string |
The id of the current user. Unset if guest. |
|
0..n |
List of permission records |
The effective list of permissions assigned to the user |
|
0..n |
List of permission records |
The list of groups assigned to the user |